ABOUT
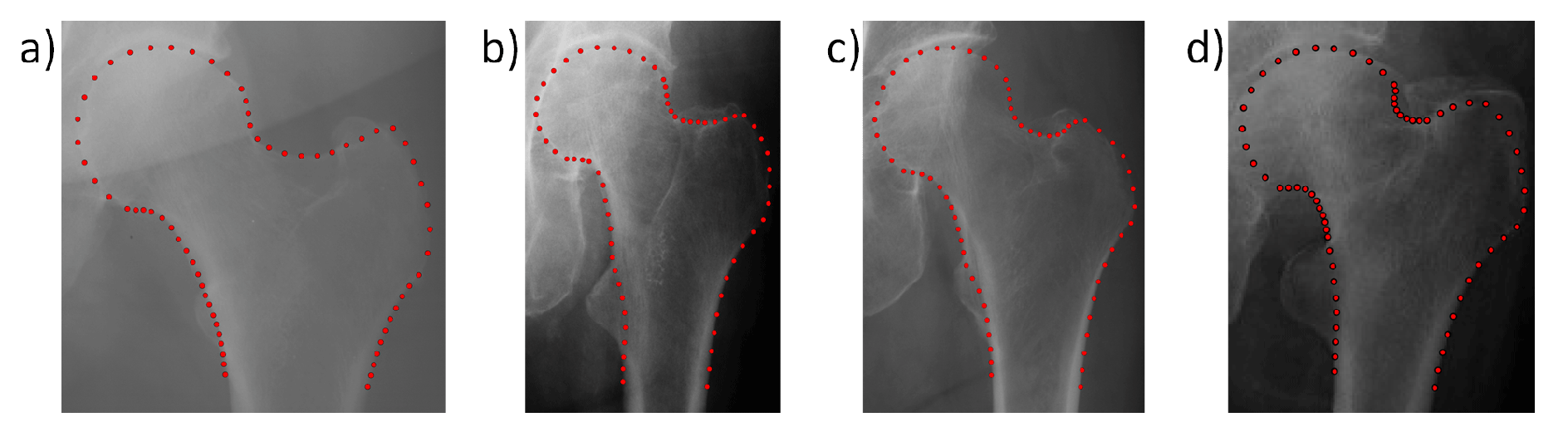
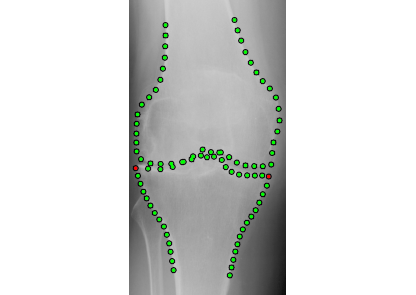
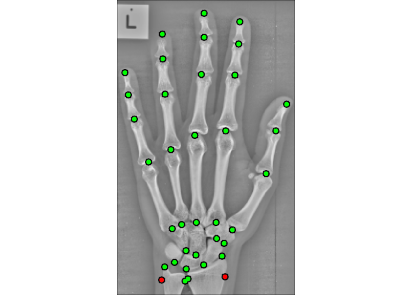
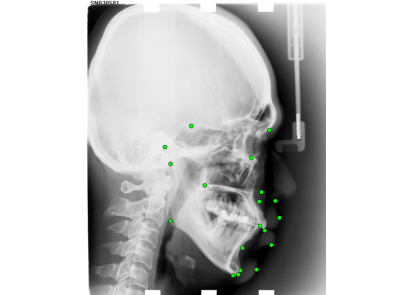
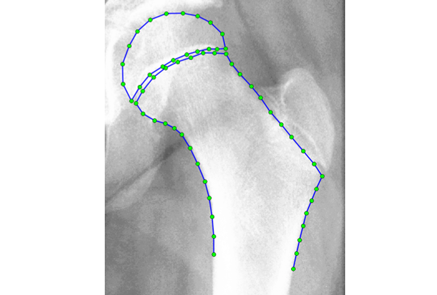
BoneFinder® is a fully automatic software tool to outline and segment skeletal structures from 2D radiographs by placing a set of points along the bone contour or at key landmark positions. It was originally designed for the segmentation of the hip joint but is now also used for other skeletal structures such as the joints of the hand or the knee joint.
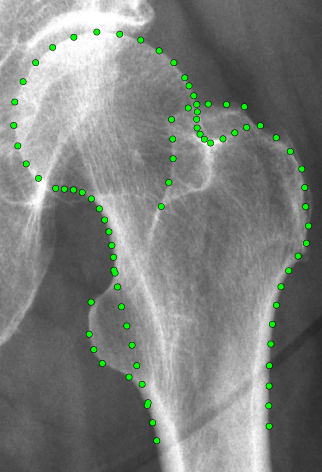
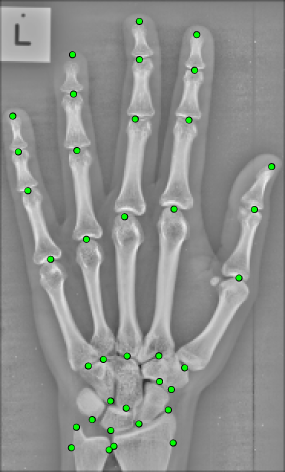
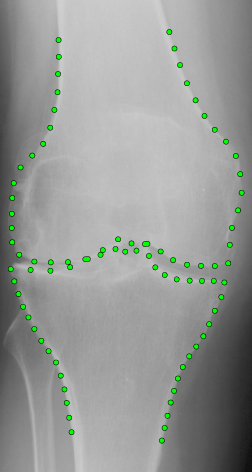
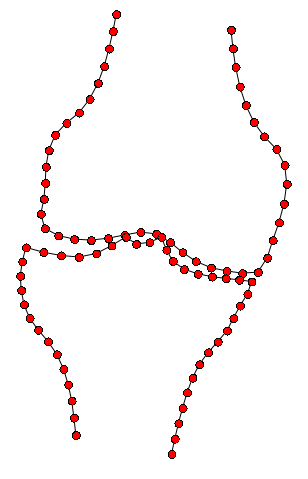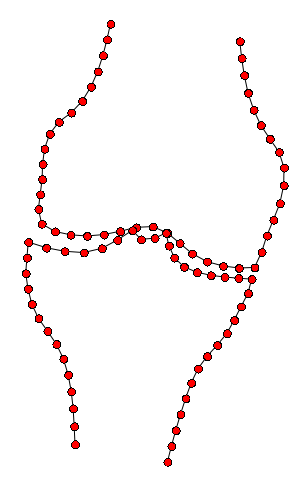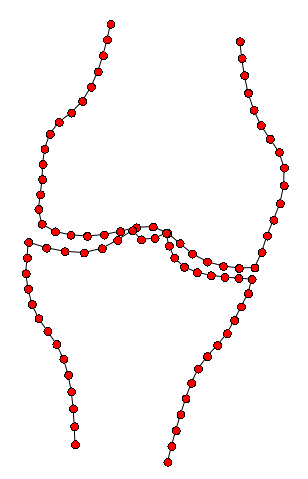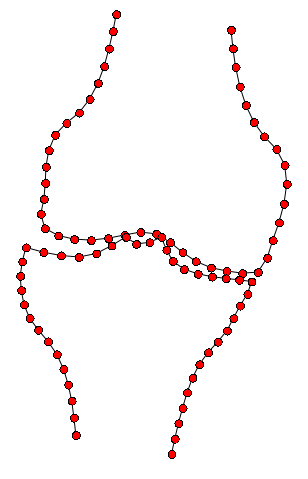
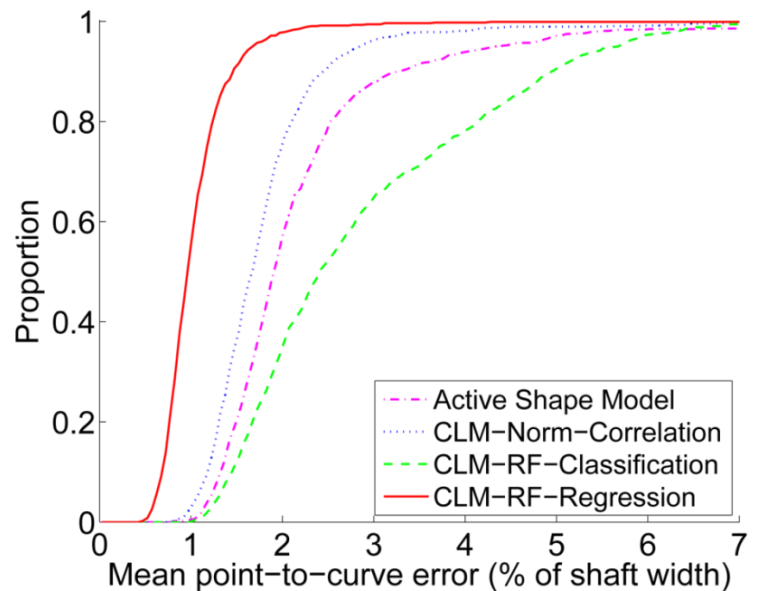
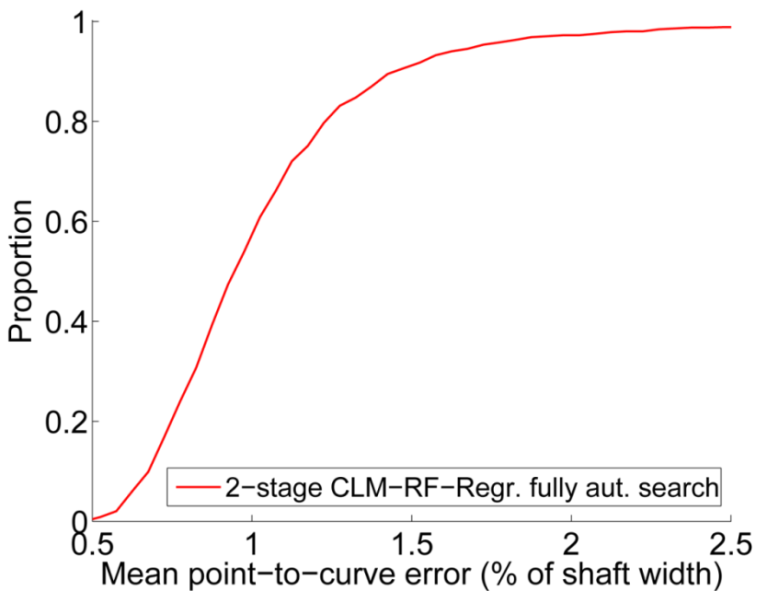
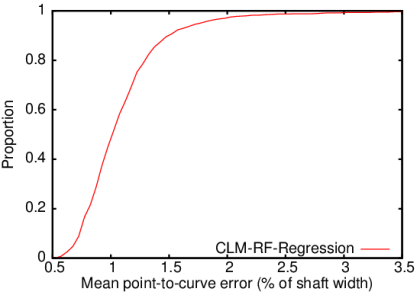
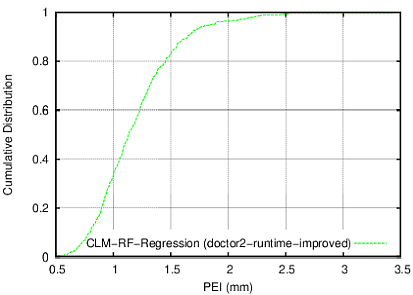
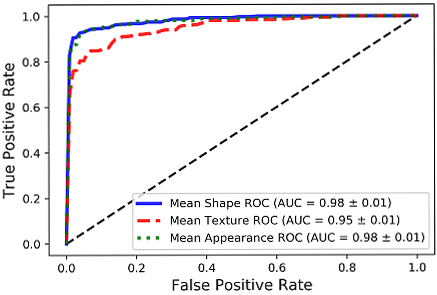
BoneFinder® firstly identifies the rough position of the bone in the image and then outlines its contour. To do so, BoneFinder® follows a machine-learning approach. This means that it has been trained on lots of examples in order to learn what to look for in an image, and it now uses this acquired knowledge to identify and segment similar bones in new unseen images. BoneFinder® has been found to lead to very robust and accurate point placements across skeletal application areas.
The resulting point positions can then be used for a range of shape analyses such as building statistical shape models or automatically deriving conventional geometric measurements.
Scientific background: BoneFinder® uses a Hough Forest like approach to detect the structure of interest in the image, and then applies Random Forest Regression-Voting in the Constrained Local Model framework to locally refine all point positions. More details on these methods and relevant references can be found in our peer-reviewed journal publications of international standing in IEEE TMI and IEEE PAMI. The underlying BoneFinder®-technology has been patented: T. Cootes, C. Lindner, M. Ionita. Image processing apparatus and method for fitting a deformable shape model to an image using random forest regression voting. Patent numbers EP 2893491 (approved for GB, FR, DE), US 9928443 (approved for US).
BoneFinder® was written by Claudia Lindner, Tim Cootes and other members of the Centre for Imaging Sciences at The University of Manchester, UK. Funding for the development of BoneFinder® has been received from the Medical Research Council UK, the Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council UK, Versus Arthritis, the Wellcome Trust and the National Institute for Health Research.